Quick Navigation
GPU Republic is reader-supported. We follow a strict editorial process and put hours of research into testing, reviewing, analyzing & comparing the best products that we can find so you can make the most informed decisions. In the event you choose to buy something from one of the links on our site, we may make a commission at no extra cost to you. Whatever products we recommend, it’s because we truly believe in them, not because of the small commission we may receive. Please don’t buy any of these products unless you actually think that it would fit your needs.
Power consumption is the one of the most important factors when it comes to shopping for gaming cards and if you are after GPUs like the GeForce RTX 3080 and GeForce RTX 3060, then you’ll need to know how much power these cards will draw under different workloads. This article will help you pick the right power supply to fuel these cards.
Generally speaking, the GeForce RTX 3080 draws more power than the GeForce RTX 3060 due to its extra CUDA cores, VRAM, and clock speed, but we are more interested to find out how much power these cards will consume when gaming, video editing, mining, or with dual monitors. Before we dig deeper, it’s important to be familiar with the “TDP” and “TGP” of a graphics card.
TDP stands for thermal design power, which is the amount of heat that is the maximum amount of power a chip can use in watts. TGP on the other hand is the total graphics power that a power supply should provide to the video card.
Importance of Power Supply for GPUs
Let’s start this way, the most power-hungry component inside your PC is the graphics card and that card will need a power source to perform its functions. Modern-day graphics cards can consume a 500 watt power supply at full load. Some even need up to three power external power connections from your PSU to run properly.
At the same time, improvements in technology have enabled AMD and Nvidia to build graphics cards with more energy efficient TDPs. Some entry-level graphics cards only require 75W to power your PCIe slot to run properly. Such graphics cards do not need an external power connection from your PSU, but even in the case that it might, your PSU has to provide the required amount of power to your PCIe slot.
Powerful graphics cards like the RTX 3080, RTX 3090, RTX 3090 Ti, and RTX 4090 come with 2 or 3 external power connections to power up as the PCI Express x16 slot on your motherboard cannot provide more than 75W of power to your video card. So, the only way around this is to provide extra power via an external power connector coming directly from the PSU.
If your power supply is too weak for your GPU, then you’ll have trouble booting up your computer or you may suffer frequent restarts. And if somehow you managed to avoid both of these issues, then your GPU likely will not perform to its full potential. As you throw some ask your graphics card to perform tasks, it’ll reach out for the power it needs to perform that task, and this may then end up crashing your system.
In such situations, you can undervolt your graphics card to lower its wattage requirements, and if you decide to do this, we have already published an undervolting guide using RX 480 to use as a reference. But if you are opting for higher-TDP graphics cards, we always advise you to upgrade your power supply. Nvidia recommends having a 750 watt power supply on your system to run RTX 3000 series cards.
Nvidia flagship chips like the RTX 3090 draw up to 350 watts alone from your energy supply, and that’s just the Founders Edition version of RTX 3090. The third-party RTX 3090s consume even more power as they are overclocked and come with more features (RGB, fans, etc). The same is the case with AMD’s RX 6000 series cards where the RX 6900 XT needs 800W of energy to properly run in its full glory. All of these power requirements can only be dealt with if you have a reliable PSU in your system.
RTX 3080 power consumption: How many watts does it use?
During our tests, we also found that the RTX 3080 consumes as low as 26W when watching movies at higher resolution, but it depends upon the type of workload that you throw at it. Using a single monitor with RTX 3080 keeps the power draw down to 11W whereas connecting dual monitors doubles these numbers to 22W and in some cases 23W (depending upon the refresh rate of the screen). Although the overall power consumption on the RTX 3080 is higher than previous generation cards, it delivers a better performance-to-watt ratio.
The power consumption of the RTX 3080 in gaming is different from content creation and other GPU-intensive tasks. Having said that, the power draw will vary depending on the gaming resolution you are playing at. So the consumption at 1080p resolution would be different from that of 1440p resolution. A power consumption test of different RTX 3000 series Founder Edition cards by Tomshardware shows that the RTX 3080 consumed 332 watts of power at 1440p resolution in a game like Metro: Exodus.
The power consumption score of the RTX 3080 was closer to the RTX 3090 which draws 361 watts at the same resolution. The TDP rating of the RTX 3080 Founders Edition is 350W, but our real-world testing showed that this can go up or down depending on the workload and resolution you are using.
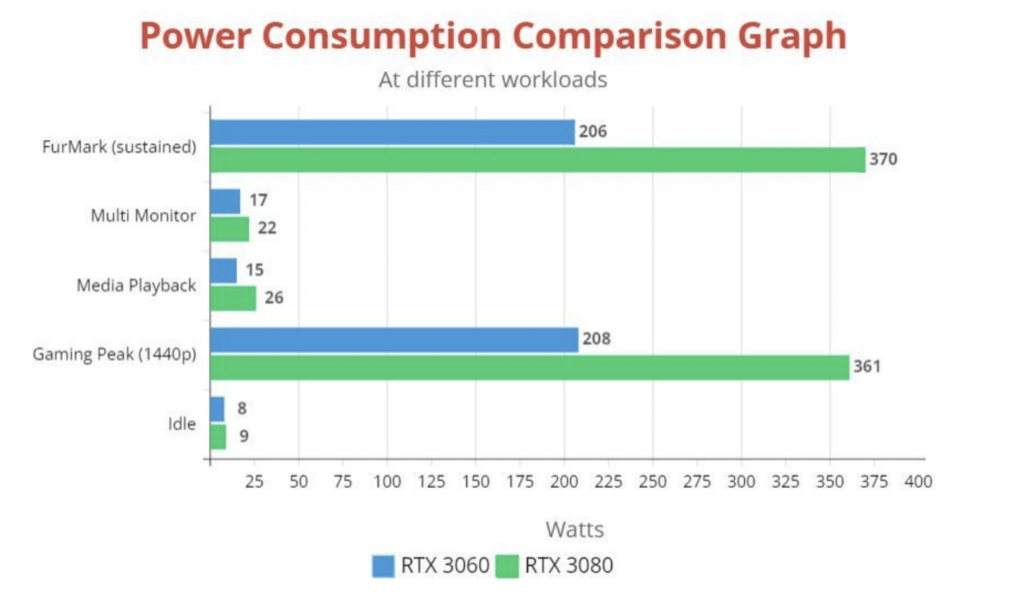
In an idle state, the RTX 3080 consumes as low as 9W of power, however, at a 1080p or 1440p gaming workload, it consumes anywhere between 300W to 361W of power. Additionally, when gaming, the power consumption also depends upon the game that you are playing as graphically intense games can put a lot of stress on RTX 3080. To find out how much power can RTX 3080 consume in rendering, we ran the FurMark test for 30 minutes. At sustained settings, the RTX 3080 the power consumption on RTX 3080 exceeds 370W.
At an idle state, the RTX 3080 consumes 4 watts of energy less than the RTX 2080 Ti, the most powerful card in the Turing architecture lineup, although while gaming, it will consume a lot of power, it will also deliver more frames-per-second (fps) on your screen at different resolutions.
What power supply should I use with my RTX 3080?
In most complex workload scenarios, the RTX 3080 consumes anywhere between 320W to 360W of energy. For such a higher power draw, you’ll need a high-wattage PSU. Nvidia recommends using a 750W PSU to safely run either GeForce RTX 3080 and GeForce RTX 3080 Ti Founder Edition cards, which is double the amount of power that an RTX 3080 card consumes at its full potential.
We also recommend you pair at least a 750W gold-rated PSU with the RTX 3080. If at the same time you have other beefy components packed inside your PC case, then you should go with an 850W PSU just to be on the safe side. Any PSU over the 850W rating would be overkill for an RTX 3080 as going with 1000W or 1200W won’t improve the performance of your RTX 3080. Here are some reliable power supplies to pair with RTX 3080 card:
- be quiet! Dark Power Pro 12
- Corsair RM750x
- Cooler Master MasterWatt 750
- EVGA SuperNOVA P2 750
It’s worth mentioning at this point the efficiency rating of a power supply. 80+ is the minimum efficiency rating that we recommend with higher-end GPUs like the RTX 3080 or RTX 3080 Ti. You can go with a Bronze 80 plus power supply if you want, however, to deliver the most power to your graphics card, it’s recommended to with at least gold or platinum-rated PSUs.
RTX 3060 power consumption: How many watts does it use?
At a 1440p gaming workload, the RTX 3060 consumes anywhere between 150W to 180W of power, however, in some demanding titles like RDR2 and Far Cry 6, these numbers soar up to 208W. During the FurMark benchmark test, the RTX 3060 consumed around 206W.
The RTX 3060 requires the least power consumption in Nvidia’s GeForce RTX 3000 family. Compared to a previous generation card like the RTX 2060, the RTX 3060 consumes a bit more power in gaming. The RTX 3060 has a TDP of 170 watts, but it can break through this limit if you put more workload on this graphics card. Just like the RTX 3080, the number of watts consumed by the RTX 3060 depends upon the task that you’ll throw its way.
We ran the same tests on RTX 3060 as we did on the RTX 3080 card, but due to fewer resources, the RTX 3060 consumes half the amount of power that the RTX 3080 does with the same workloads. Non-gaming power consumption of RTX 3060 is similar to that of other RTX 3000 cards & in an idle state, it consumes as low as 8W of power. Playing higher resolution files on the RTX 3060 spikes the power consumption up to 15W and if you connect two higher refresh monitors to your RTX 3060, it will pull 17W from your PSU.
What power supply should I use with an RTX 3060?
Nvidia recommends using a 550W PSU for the RTX 3060, but this recommendation is limited to the Founders Edition of RTX 3060. If you are buying an AIB version RTX 3060 from EVGA, ASUS, or GIGABYTE that is factory overclocked or has more RGBs and stuff on it, then you’ll need a higher wattage PSU something like a 650 watt power supply. A 550W supply will do the job, but a 650W unit will make sure that there’s enough power left behind in case your RTX 3060 needs it.
Through our power consumption tests, we’ve concluded that the RTX 3060 can consume up to 208W when gaming or rendering files. From our experience, these are the most suitable PSUs to fuel the RTX 3060.
RTX 3080 vs RTX 3060 power consumption comparison
From the results that we’ve concluded through our tests, it’s evident that the RTX 3060 consumes less power than the RTX 3080. When idle, the difference in power consumption is miniscule. The metrics at an idle state reflect Nvidia’s effort to reduce the power consumption of the Ampere lineup.
Both cards consume less than 10W when there’s no workload thrown upon them and these numbers remain below 30W if you stream some HD videos on YouTube or Netflix. However, the RTX 3060 still consumes 10W less power than the RTX 3080 in media playback.
Adding a second monitor to both of these cards doesn’t move the power consumption metrics away from the idle state; the RTX 3080 draws an extra 5W compared to the RTX 3060 if you connect a second display to it. But stress testing these cards shows us a different story. The RTX 3080 pulls more power out of your power supply when gaming at 1440p resolution, while the RTX 3060 draws almost half the amount of power when you play the same game at 1440p resolution. All this said, the extra power that the RTX 3080 consumes results in higher FPS in gaming as compared to the RTX 3060, so it’s a tradeoff that you should consider.
Best power cables for the RTX 3080 & RTX 3060
Almost every card in the RTX 3000 family needs one or two external power connections from your power supply. The RTX 3060 Founders Edition requires one 12-pin power connector, while some AIB versions of the RTX 3060 come with 8-pin and 6-pin power input. The RTX 3080 on other hand requires two 8-pin power inputs to run, but this can also vary depending on the AIB version you are about to buy.
Power cables or modular cables are also included in the GPU box, but if there are no cables included by the seller, then you’ll have to buy aftermarket power cables. Here are some good options to consider:
MICRO CONNECTORS Premium Sleeved Cable
source: amazon
This cable comes with one 12-pin power connection at one end and two 8-pin power connectors at the other end to power up cards like RTX 3080 and RTX 3060 from different manufacturers. It’s a 30cm long cable made that can be connected either to a modular or semi-modular power supply.
COMeap GPU VGA PCIe
source: amazon
In case you have a non-modular power supply in your system that has enough power to run an RTX 3000 series card, then these male/female power converters can help you power up your graphics card. You can connect the female 8-pin end to the male 8-pin end of your non-modular or semi-modular PSU. Similarly, the other two (6+2) male ends will work for the graphics card. You can use the two 8-pin configurations on this cable for an RTX 3080 or you can plug in the two six-pin connectors to power up an RTX 3060.
QINGSEA Q Power Extension Cord
source: amazon
This is a 12-pin to two 8-pin Molex power cable to fuel the RTX 3000 series family of video cards. It’s highly compatible with any of the RTX 3060/RTX 3060 Ti/RTX 3070/RTX 3070 Ti/RTX 3080/RTX 3090 graphics cards.It’s 300mm in length, which is long enough to reach from any end inside your PC case. The QINGSEA power cable is made up of high-quality mesh sleeves for easy cable management.
Methods we used for measuring power consumption
To find out accurate power draw, Cybernetics has developed a system called Powenetics that makes use of sensors to measure the power draw between the PCIe slot and power connectors coming from the energy supply. It’s the same system that’s used by Tomshardware and other reviewing platforms to determine the power draw efficiency of a graphics card. In addition to the Powenetics kit to measure the power efficiency, we have opted for higher-end specs so that our both GPUs do not run into a bottleneck. Our test system consists of a Core i7 12700K CPU, ASUS ROG Strix Z690-F motherboard, 32GB DDR4 RAM, Samsung EVO M.2 SSD, and an 850W Cooler Master power supply.
Most other reviewers use the full PC power draw method to find out the power consumption of different graphics cards, but using this method only shows the power draw at full load and idle state. Also, this only gives you a rough idea about the power efficiency of a GPU.
Another method used to measure power consumption is via third-party software like GPU-Z or HWiNFO64, however, the power results from such tools are generally less than the full board power. For graphics cards like the RTX 3080 & RTX 3060 that draw most of their energy from power supplies other than PCIe, you may not get the right power draw metrics from these methods.

Hi, I’m the author and founder of this blog. I have more than 10 years of experience in the industry. Throughout my journey I’ve tested and reviewed hundreds of graphics card for custom PC builds. I believe my knowledge and experience will help you choose the card that really falls to your needs and budget.